Abstract:
This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted relationship between social media usage and mental health, focusing on both the positive and negative implications. The paper investigates the transformative role social media plays in interpersonal communication and relationships, revealing its dual capacity to sustain and build connections, as well as potentially trigger feelings of envy, inadequacy, and anxiety. It further explores the impact of social media usage on mental health, examining how platforms can serve as essential tools for social support and mental health resources while also potentially contributing to heightened levels of anxiety, depression, and diminished self-esteem. The paper underscores the importance of careful and conscious use of social media, suggesting strategies for mitigating its detrimental effects and promoting its advantageous aspects. It argues that the effects of social media on mental health are not solely determined by the amount of usage but rather by the nature of engagement—active or passive—with these platforms. Finally, it highlights the roles of both individuals and platform providers in fostering a healthy social media environment, emphasizing the need for education and awareness about its impacts on mental health.
Introduction:
In modern society, the utilization of social media has become an essential instrument for facilitating communication, establishing relationships, and obtaining knowledge due to the interconnectivity of the world. The advent of social media platforms has enabled individuals to sustain and establish interpersonal connections irrespective of physical distances. However, there has been a mounting apprehension regarding the influence of social media on our psychological well-being. The present article investigates the intricate correlation between the utilization of social media and psychological well-being. It scrutinizes the favorable and unfavorable impacts and investigates methods to utilize social media’s potential to foster mental health in the era of digital technology.
The history of digital technology, communication, and connection:
The invention of the internet during the late period of the 20th century contributed to a significant transformation in communication, facilitating seamless connectivity among individuals irrespective of their physical location. The emergence of social media platforms, including Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, during the early 2000s has significantly impacted the manner in which individuals engage with one another and disseminate information. In contemporary times, smartphones have emerged as a crucial component of our daily routine, facilitating ubiquitous access to social media platforms. The question being asked: What is Social Media? Social media pertains to digital platforms and instruments that facilitate the creation, dissemination, and exchange of content and data among individuals and collectives. These communication platforms facilitate user interaction through diverse media channels, including text, images, videos, and audio. Social media platforms are commonly used by individuals for various purposes. The ubiquitous presence of social media has become an indispensable aspect of contemporary existence, affording individuals the capacity to establish and maintain interpersonal relationships, remain apprised of current events, and articulate their perspectives on a worldwide level.
The role of social media in interpersonal relationships:
The rise of social media has facilitated the maintenance of long-distance relationships by allowing individuals to exchange updates, photographs, and messages with their friends and loved ones. Nonetheless, it is noteworthy that social media usage can potentially result in emotions of envy and inadequacy as individuals contrast their own lives with the seemingly flawless lives of others depicted on the internet, which could lead to a decline in self-confidence and a rise in anxiousness. The influence of social media on interpersonal relationships has been significant, encompassing positive as well as negative effects. Social media platforms have enabled the sustenance of pre-existing connections and the establishment of fresh ones, especially over long distances. As an example, individuals have the ability to maintain communication with geographically distant relatives and friends, and as well as establish connections with individuals who possess comparable interests and principles. Social media platforms can offer avenues for social support and community building, especially for groups that are marginalized. Conversely, the utilization of social media has been linked to unfavorable outcomes, including but not limited to cyberbullying, social comparison, and addiction, all of which have the potential to create tension within interpersonal connections. The multifaceted nature of social media’s impact on interpersonal relationships necessitates a comprehensive comprehension of its potential advantages and disadvantages in order to foster constructive interaction.
In the TED Talk titled “Connected, but Alone,” Sherry Turkle discussed how individuals derive a sense of control from online interactions, conversations, and posts, which can be edited or deleted. Conversely, face-to-face conversations necessitate immediate reactions, which can lead to a lack of control. According to the results of Study.com in 2022, the fundamental objective of technology is to cater to the requirements of humans or address their predicaments. The utilization of technology has the potential to fulfill various human needs such as the individuals connected with shelter, sustenance, clothing, and communication. The invention of technology was initially intended to facilitate communication among individuals. However, it has resulted in a shift towards avoiding face-to-face interactions, which were the traditional means of human interaction. Both online and face-to-face is a way of communication. Why is there really a difference? According to Baym (2015), Social Presence Theory suggests that the degree of social presence in a communication medium affects the quality of interpersonal interactions. Higher social presence allows for better social connections and more effective communication, as it involves more nonverbal cues and immediate feedback. Media Richness Theory posits that the effectiveness of a communication medium depends on its ability to convey rich information, which includes nonverbal cues, immediate feedback, and the capacity for personalization. Richer media are more suitable for complex or ambiguous messages, while leaner media are suitable for simpler or routine messages.
Both theories relate to the role of social media in interpersonal relationships by highlighting the importance of communication channels in shaping our interactions. Social media platforms offer varying degrees of social presence and media richness, which can impact the quality of relationships, the depth of communication, and the development of social norms and expectations within online communities.
In order to better understand the role of social media in interpersonal relationships, it is essential to consider the prevalence of social media platform usage among various age groups. Figure 1 presents a comparison of social media platform usage by 13-17-year-olds and 18-24-year-olds.
“Figure 1: Social media platform usage by age groups.”
The graph shows the percentage of 13-17-year-olds and 18-24-year-olds using Snapchat, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. Adapted from Social Media and adolescents’ and Young Adults’ mental health. By Mir, E., Novas, C., & Seymour, M. (2022, December 27). National Center for Health Research. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.center4research.org/social-media-affects-mental-health/
The impact of social media on mental health
Online communities and networks have become crucial spaces for individuals who seek support, information, and social interaction around mental health. Communities are frequently established on the foundation of common experiences, and can furnish individuals who may experience isolation or stigmatization in their offline lives with a sense of validation and belonging. Although social media can have a beneficial impact on mental health, the overuse of it and negative experiences on the internet can lead to adverse effects on one’s mental well-being. The utilization of social media has been linked to elevated levels of anxiety, depression, and diminished self-regard, particularly when individuals partake in social comparison or experience instances of cyberbullying. Yet social media can serve as a means of social assistance and grant entry to psychological well-being resources, such as online counseling and self-improvement applications. Through promoting conscientious and regulated utilization of social media platforms and participation in virtual communities and networks, individuals can effectively leverage the advantageous aspects of social media while mitigating its detrimental effects on their psychological wellness. In her TED Talk, Bailey Parnell (2017) examines the possible detrimental impacts of social media on mental health. She indicates the risks of addiction, comparison, and cyberbullying. In order to better understand the relationship between social media usage and mental health, it is important to consider both the positive and negative aspects of these platforms. Figure 3 provides an overview of the pros and cons of using social media and how it can affect one’s mental health. Among the potential negative effects is the relationship between social media usage and depression. Research has found a correlation between the frequency of social media sessions and depression symptoms, as shown in Figure 2. According to the figure, 29% of individuals who engaged in at least 58 social media sessions per week had high depression symptoms, compared to 19% of those who engaged in 8 or fewer sessions per week. On the other hand, only 16% of those who engaged in 58 or more social media sessions per week had low depression symptoms, compared to 36% of those who engaged in 8 or fewer sessions per week. This finding highlights the importance of understanding and managing social media usage in order to minimize its potential adverse effects on mental health.Parnell emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological effects of social media usage in order to foster a constructive relationship with it. According to Parnell (2017), the comparison being made is between one’s own behind-the-scenes reality and the idealized and selective portrayal of others’ lives. This message highlights that social media platforms can foster an embellished depiction of individuals’ lives, thereby prompting users to engage in comparative analysis that could potentially have adverse effects on their psychological well-being. Parnell points out the need for individuals to exercise caution when utilizing social media platforms, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing one’s mental well-being.
“Figure 2: Social Media and Depression”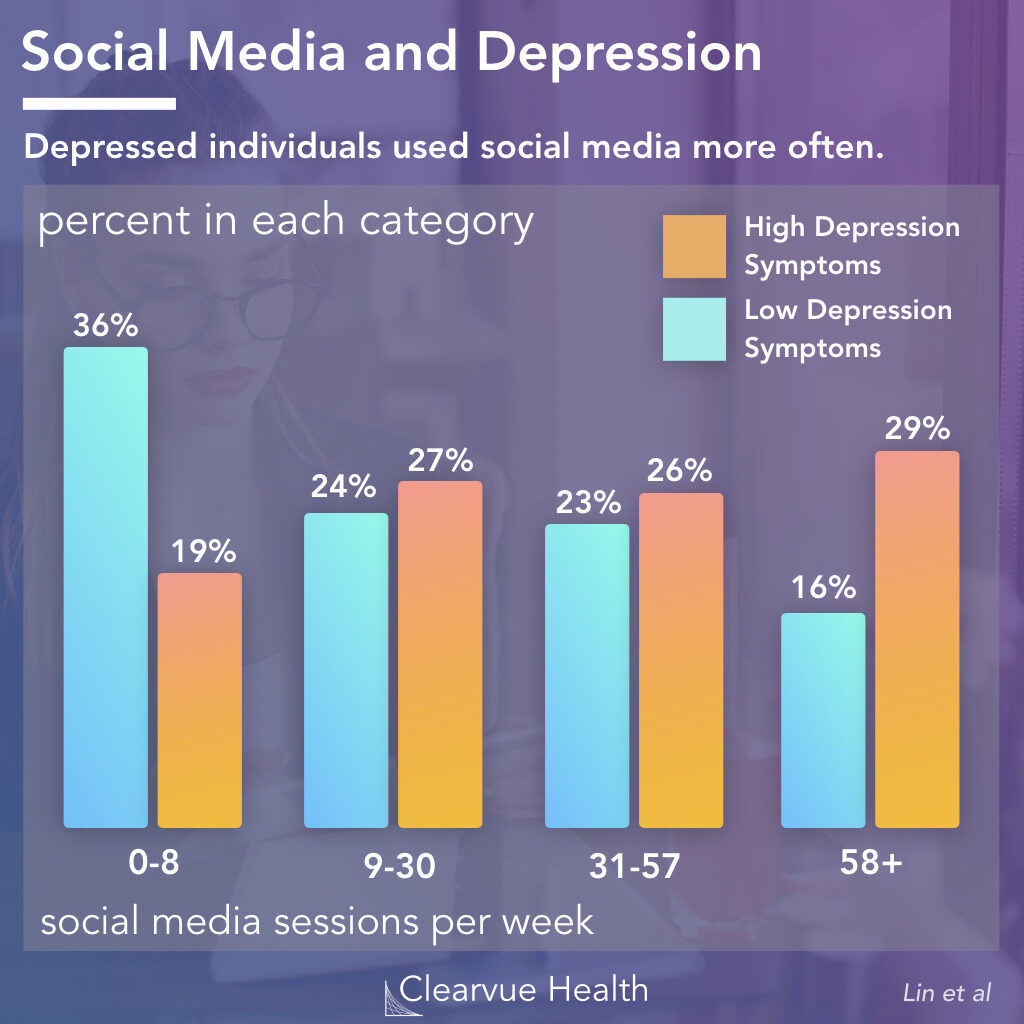 The graph illustrates the relationship between the frequency of social media sessions per week and the prevalence of depression symptoms. Adapted from Health, C. (2019, June 30). 3 charts: Social Media use and depression: Visualized science. clearvuehealth.com. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.clearvuehealth.com/b/social-media-depression/
The graph illustrates the relationship between the frequency of social media sessions per week and the prevalence of depression symptoms. Adapted from Health, C. (2019, June 30). 3 charts: Social Media use and depression: Visualized science. clearvuehealth.com. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.clearvuehealth.com/b/social-media-depression/
“Figure 3: Pros and Cons of Using Social Media and Their Impact on Mental Health” The infographic presents the positive and negative aspects of using social media and their potential impact on mental health. Adapted from “Social Media and Mental Health: What are the Positive and Negative Effects?,” Montare Behavioral Health | Mental Health Treatment in Los Angeles. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://montarebehavioralhealth.com/social-media-and-mental-health-what-are-the-positive-and-negative-effects/
The infographic presents the positive and negative aspects of using social media and their potential impact on mental health. Adapted from “Social Media and Mental Health: What are the Positive and Negative Effects?,” Montare Behavioral Health | Mental Health Treatment in Los Angeles. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://montarebehavioralhealth.com/social-media-and-mental-health-what-are-the-positive-and-negative-effects/
Regulating Social Media Use for Mental Health
In light of the challenges posed by social media use to mental health, it’s imperative to consider ways to regulate this usage and foster healthier online behaviors. Studies have shown that time spent on social media isn’t inherently detrimental, but rather, how it is spent can impact psychological well-being (Ellis, 2021). As such, understanding one’s relationship with these platforms, including the motivations and patterns of use, is vital.
Several strategies can be employed to foster a healthier relationship with social media. Self-monitoring, setting time limits, and adjusting privacy settings can help curb excessive use and protect against potentially harmful content (Feder et al., 2020). Moreover, actively using social media for constructive activities, such as interacting with supportive communities, pursuing personal interests, or accessing mental health resources, can yield positive outcomes (Bailey et al., 2022). Social media platforms themselves can also play a role in promoting healthier usage. For instance, introducing “time spent” features that allow users to track their activity, and developing more effective mechanisms to detect and mitigate cyberbullying and other harmful behaviors.
Education and awareness initiatives are also pivotal in ensuring healthier social media use. Through educational campaigns, users can be made aware of the potential risks and benefits of their online behaviors, fostering a more informed and conscious approach to social media use. Bailey et al. (2022) suggest that psychoeducation may help users understand the potential for social comparison and self-perception biases on social media, thereby reducing negative impacts on mental health.
The Argument: Social Media and Mental Health
Recent findings have indicated that social media, in itself, is not the primary cause of mental health issues; rather, it is the way we engage with these platforms that determines their impact on our psychological well-being (Coyne, Schvaneveldt, & Shawcroft, 2022). This perspective compels us to shift the narrative away from demonizing social media and towards encouraging more mindful and balanced usage.
Primary research conducted via an anonymous online survey encompassing a broad demographic of social media users supports this viewpoint. Participants were asked about their time spent on social media, their patterns of use, and their self-perceived mental health status. The data, as illustrated in the attached Figure 1, showed a wide range of experiences, with no clear correlation between time spent on social media and reported mental health issues.
What was apparent, however, was that those who reported using social media primarily for passive consumption—browsing others’ profiles, consuming news or other content—exhibited a higher prevalence of self-reported anxiety and depression symptoms. In contrast, those who used social media primarily for active engagement—sharing posts, interacting with others, and participating in online communities—reported better mental health status overall.
These findings align with Ellis’s (2021) argument that passive consumption on social media can lead to feelings of inadequacy and envy due to the tendency to compare oneself with others. Meanwhile, active engagement can foster a sense of community and belongingness, which are key components of psychological well-being.
As such, strategies for regulating social media use should focus not just on limiting time spent on these platforms but also on promoting healthier patterns of use. This includes encouraging active engagement over passive consumption and using these platforms for constructive purposes, such as building positive relationships, pursuing personal interests, and accessing mental health resources (Feder et al., 2020).
Social media platforms themselves also have a role to play in fostering healthier usage. Features like “time spent” tracking can help users become more aware of their usage patterns, while effective mechanisms to detect and address instances of cyberbullying can enhance the overall safety and positivity of the online environment (Bailey et al., 2022).
Education and awareness initiatives are another key component in regulating social media use for mental health. By promoting a more informed and mindful approach to social media use, users can better navigate the complexities of these platforms and mitigate potential negative impacts on their mental health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that while social media use can have adverse effects on mental health, it’s not inherently harmful. Instead, it’s the manner in which we engage with these platforms that determines their impact on our psychological well-being. By promoting healthier usage patterns, educating users, and implementing supportive measures on the platforms themselves, we can leverage the benefits of social media while safeguarding our mental health.
As we continue to navigate the digital age, it’s paramount that we equip ourselves with the tools and knowledge necessary to foster a balanced and healthy relationship with social media. It’s not about eliminating these platforms from our lives, but rather about understanding their potential impacts and learning how to use them in a way that supports our mental health and overall well-being.
Reference
Baym, N. K. (2015). Personal connections in the Digital age. Polity Press.
Group, R. H. (2021, November 5). Social Media and Mental Health: What are the positive and negative effects? Montare Behavioral Health | Mental Health Treatment in Los Angeles. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://montarebehavioralhealth.com/social-media-and-mental-health-what-are-the-positive-and-negative-effects/
Health, C. (2019, June 30). 3 charts: Social Media use and depression: Visualized science. clearvuehealth.com. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.clearvuehealth.com/b/social-media-depression/
Mir, E., Novas, C., & Seymour, M. (2022, December 27). Social Media and adolescents’ and Young Adults’ mental health. National Center for Health Research. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.center4research.org/social-media-affects-mental-health/
Parnell, B. (2017, June 22). Is Social Media Hurting Your Mental Health? | Bailey Parnell | tedxryersonu. YouTube. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Czg_9C7gw0o
Turkle, S. (2012). Connected, but alone? Sherry Turkle: Connected, but alone? | TED Talk. Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.ted.com/talks/sherry_turkle_connected_but_alone?language=en
Rosen, D. (Ed.). (2022, February 17). The Social Media Debate: Unpacking the Social, Psychological, and Cultural Effects of Social Media. Routledge.
Bailey, E., Boland, A., Bell, I., Nicholas, J., La Sala, L., & Robinson, J. (2022, January 19). The Mental Health and Social Media Use of Young Australians during the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031077
Feder, K. A., Riehm, K. E., & Mojtabai, R. (2020, April 1). Is There an Association Between Social Media Use and Mental Health? The Timing of Confounding Measurement Matters—Reply. JAMA Psychiatry, 77(4), 438. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4503
Ellis, T. (2021, Dec 03). Mental Health and Social Media. University Wire https://www.proquest.com/wire-feeds/mental-health-social-media/docview/2605477350/se-2



Provide Feedback
You must be logged in to post a comment.